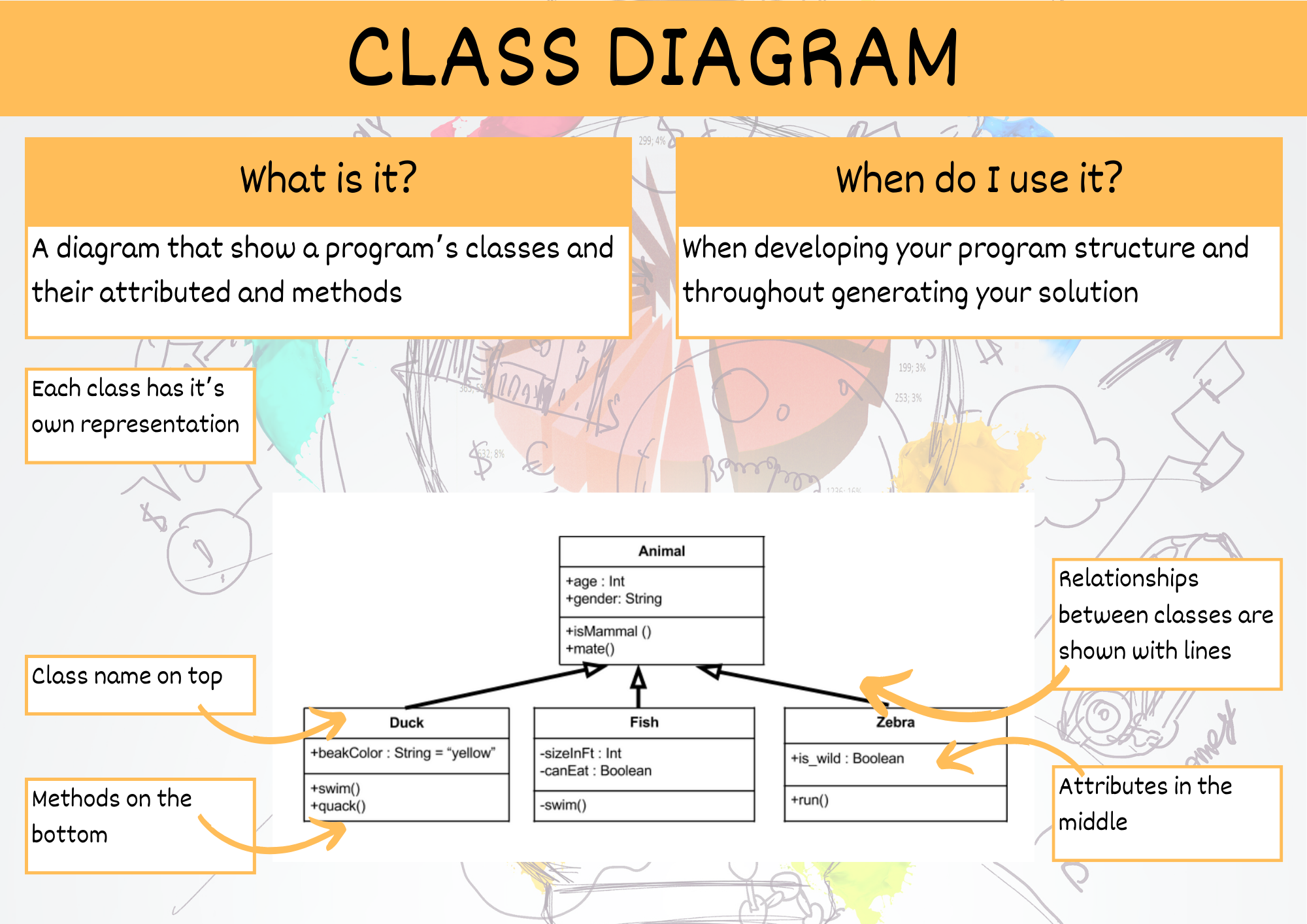
Class Diagram#
Class diagrams clearly map out the structure of a particular system by modelling its classes, attributes, operations, and relationships between objects [Lucidchart, 2017].
Class diagrams are particularly useful when using Object Orientated Programming.
The standard class diagram is composed of three sections:
Upper section: Contains the name of the class. This section is always required.
Middle section: Contains the attributes of the class. Use this section to describe the qualities of the class.
Bottom section: Includes class operations (methods). Displayed in list format, each operation takes up its own line.
Class Diagram Symbols#
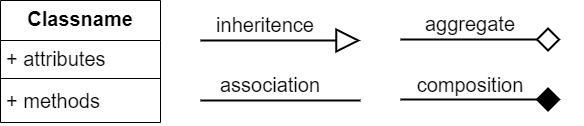
Checking the Class Diagram
When marking a Class Diagram the following questions are asked:
Are all the code’s classes represented?
Does the diagram’s attributes match the variables in the class’
__init__method?Does the diagram’s methods match the class’ methods?
Summary#
Unit 1 subject matter covered:
Symbolise algorithms and interrelationships with sketches and diagrams [QCAA, 2017]
Unit 2 subject matter covered:
Symbolise well-ordered and unambiguous algorithms using pseudocode for procedural code that processes data for insertion into a database or manipulates or displays retrieved data
Symbolise well-ordered and unambiguous algorithms using pseudocode for user interaction, data validation and data presentation [QCAA, 2017]
Unit 3 subject matter covered:
Generate a conceptual model of a possible solution by applying systems thinking that identifies system boundaries, properties, inputs and outputs, user interface, system controls
Recognise and describe program components such as objects, event handlers and multimedia assets [QCAA, 2017]
Unit 4 subject matter covered:
Symbolise and explain how application sub-systems, e.g. front end, back end, work together to constitute a solution [QCAA, 2017]
