Managing and Manipulating Data#
The set of operations that allows you to manage data in a computer system is referred to by the acronym CRUD. CRUD stands for Create, Read, Update, and Delete. It is a fundamental concept in the world of databases and computer systems.
Create: This is where you make new entries or records. Think of it like writing a new post on a social media platform. You’re creating new data.
Read: This is about retrieving or looking at the data you’ve created or stored. It’s like reading a post or checking your messages on that same social media platform.
Update: Sometimes, you might need to change something in the data you’ve created. For instance, if you made a typo in a post, you can update it to correct the mistake.
Delete: This is straightforward—it means removing data. If you decide you don’t want that post on social media anymore, you can delete it.
Structured Query Language#
SQL is a standard language for storing, manipulating and retrieving data in databases [W3Schools, 2019].
SQL is the the most popular language for working with databases despite being over 50 years old. It is everywhere and every major IT platform uses it. Why? Because it is powerful and effective.
We have covered some SQL in previous subjects, check here for a refresher.
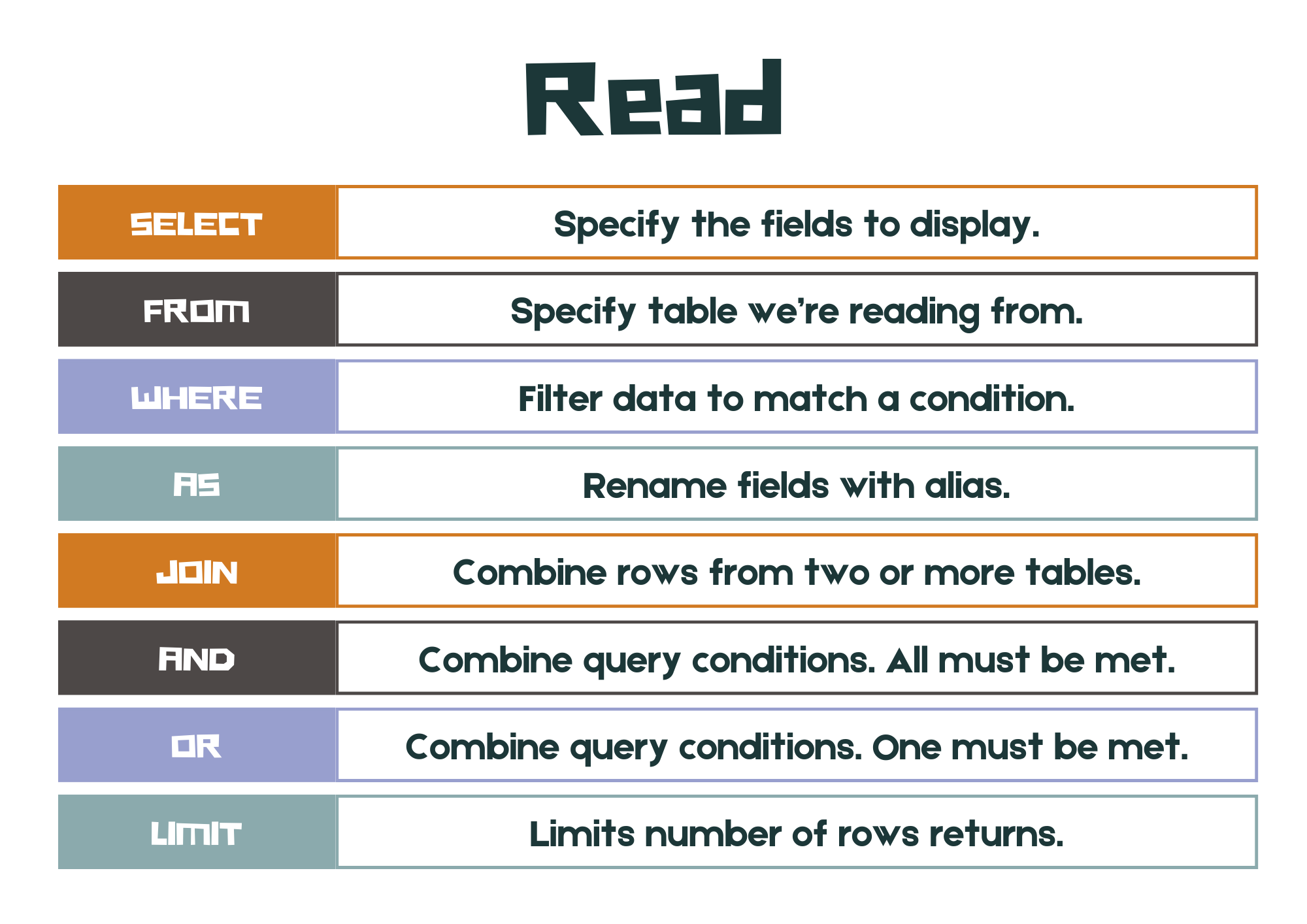
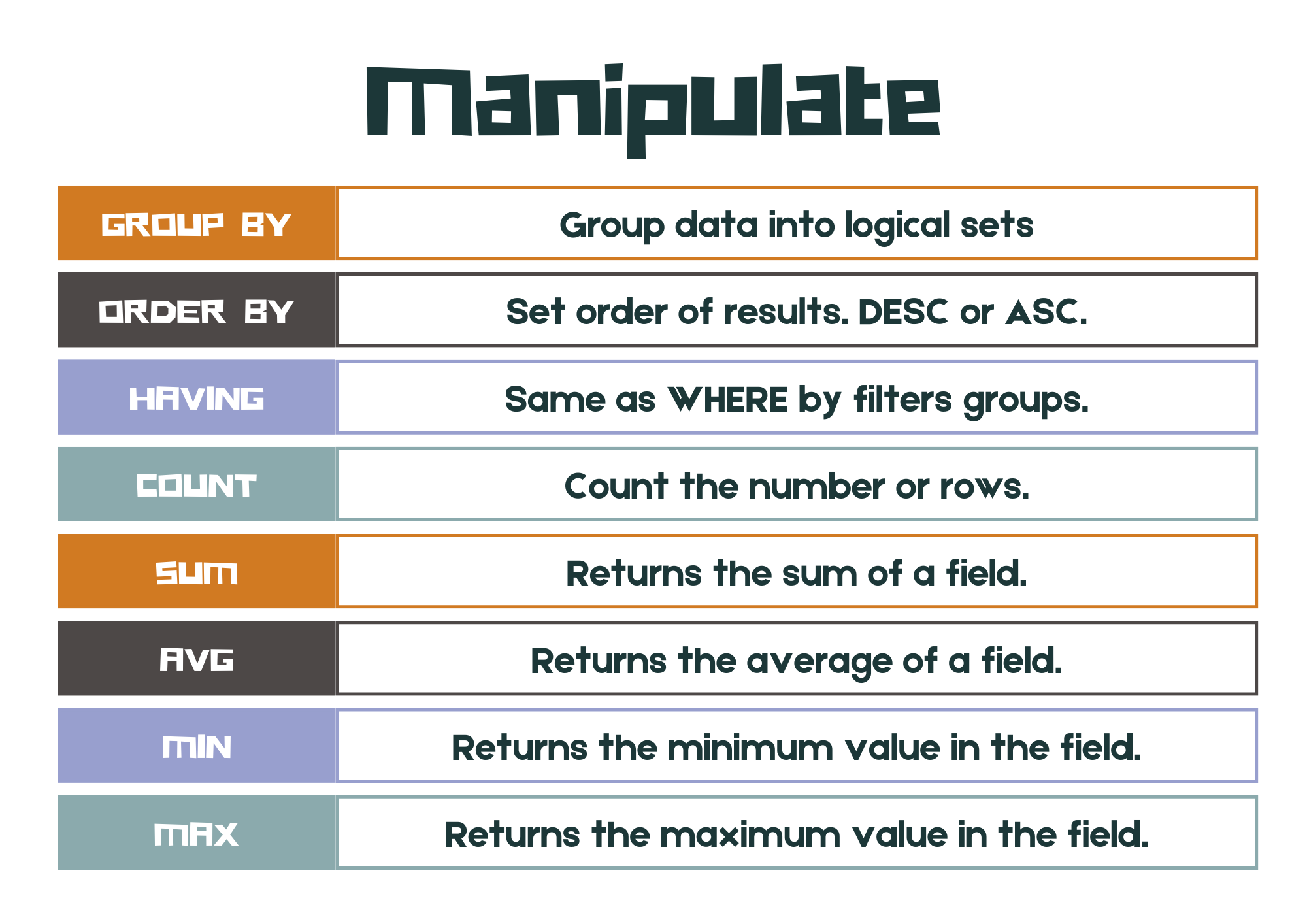
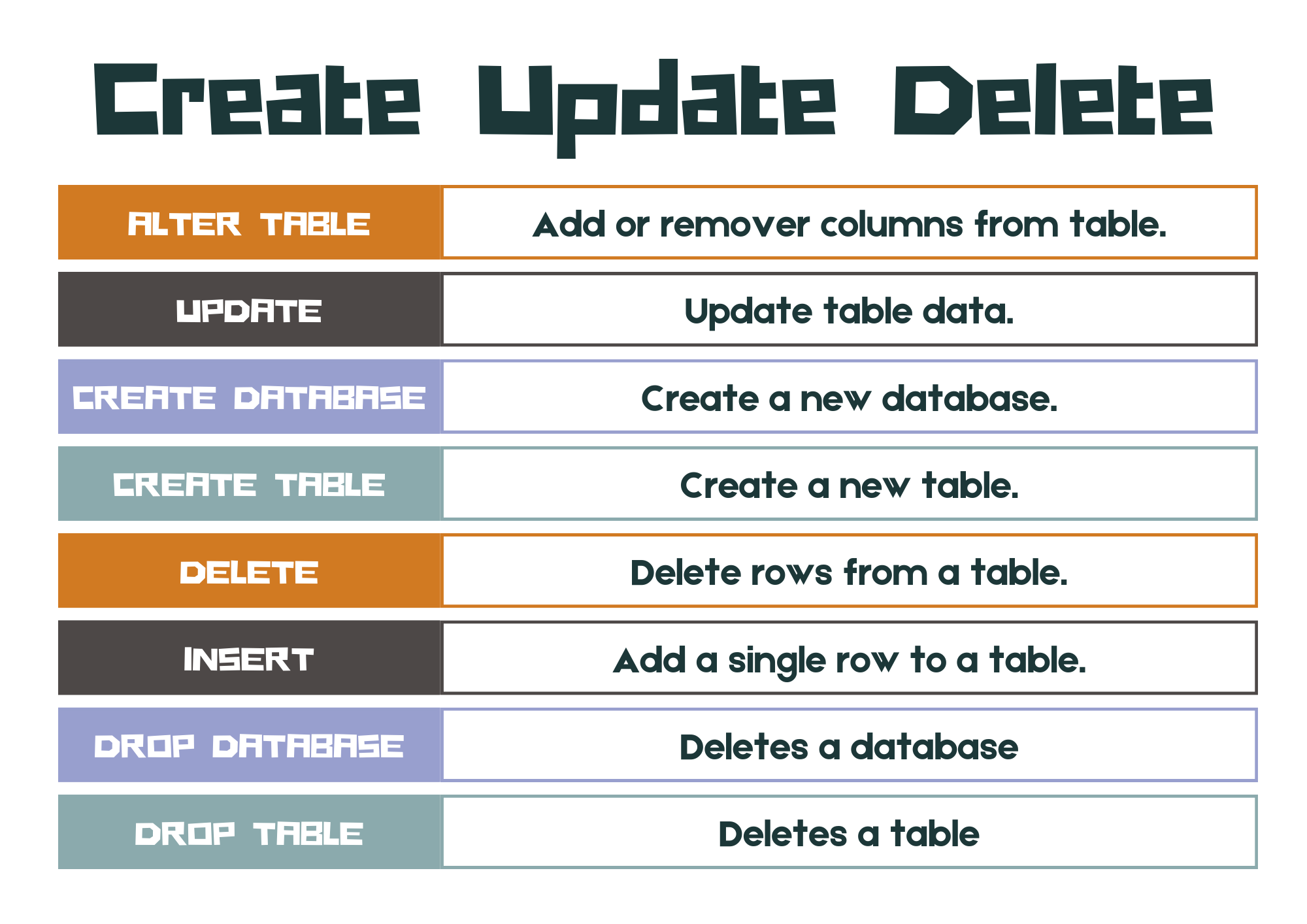
SQL has #### basic operations:
SELECT: performs queries on the database to extract tables of data
CREATE DATABASE: initially establishes a database
CREATE TABLE: makes a table in an existing database, including establishing relationships between tables
DROP DATABASE: completely delete an existing database, resulting in the loss of all data stored in the database
DROP TABLE: completely delete an existing table, resulting in the loss of all data stored in the table
ALTER TABLE: changes the structure of an existing table, including adding, deleting or modifying columns and modifying relationships
INSERT: add a row to an existing table
UPDATE: modify the data in a row of an existing table
DELETE: remove a row from an existing table
SQLite#
There are many different flavours of SQL. Most of these work by setting up an SQL server separate from the computer running the program. We will be using SQLite as our SQL database. It is a lightweight and fast database management system, which can run off a file stored on your local machine. For example, both Android and iOS use SQLite databases extensive to store app data on phones.
Unit 2 subject matter covered:
Recognise the elements needed for a data-driven solution, including programming requirements, e.g. SQL and algorithms
understand SQL syntax and use SQL statements to solve a problem [QCAA, 2017]
