Unit 2: Test Code
Contents
Unit 2: Test Code#
Code Testing#
Code testing should be completed by the developer. In testing the code you need to ensure that it is:
Reliable
Maintainable
Efficient
Reliability#
Testing reliability involves the determining the probability of a program producing an error or failing to process a task. Unit tests and integration testing will determine the effectiveness of you code, but reliability also depends on preventing users from making mistakes. For example, preventing the entering of values outside the expected range.
These consideration need to be incorporated into your unit and integrated testing.
Maintainability#
We will be using two tools to test and improve the maintainability of our code. Both tools are used extensively by Python Developers.
Sourcery#
Sourcery is leverages AI and provides metrics assessing your code.
To need to go to the Sourcey website to sign-up and receive your access token. You can then install the VS Code extension.
With the extension installed you can hover over functions def statements and a pop-up will provide metric on your code, as well as suggest ways of improving the code.
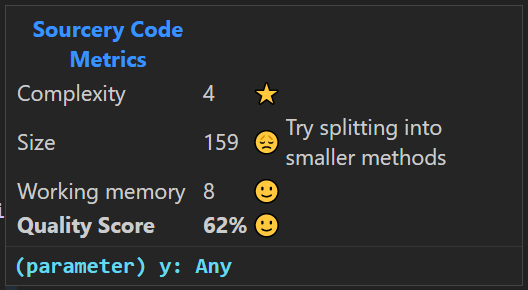
Sourcery’s code metrics:
Complexity: a measure of how difficult your code is to read and understand (lower is better).
Size: a measure of how long each method is. It is better for methods to be concise and to do one thing, so this metric penalises overly long methods (lower is better).
Working memory: a measure of the number of variables that need to be kept in your working memory as you read through the code (lower is better).
Quality: overall score for the function (higher is better)
Each function is given a score and a rating:
Star: Excellent
Smiling face: Good
Frowning face: Poor
No not enter: Bad
When completing your unit tests make sure that your include the metrics for each function.
Black#
Black is the uncompromising Python code formatter, which will ensure that your code formatting is compliant to PEP8. Ensuring your code is PEP8 compliant improves the readability of your code.
To install Black use pip:
python -m pip install black
To run simply call Black and point it to your project directory.
black .
Black should be run at the conclusion of your coding.
Efficiency#
In industry, efficiency testing is undertaken through the process of code reviews. In code reviews, the developer works with another developer to assess the efficiency of the code. For us, you will need to undertake your won review.
In testing your code for efficiency, you need to ensure your code:
has no unnecessary code
uncalled methods / functions
unused variables
unused imports
has no unnecessary reading and writing to the drive.
uses reusable components wherever possible
uses atomic modularisation (each function only does one thing)
uses error and exception handling at all layers of software
ensures data integrity and consistency
make use of coding practices applicable to the related software
Useability Testing#
Useability testing should be completed by the developer and other users. Those features that can be tested using objective measures and tools (eg. perceivability of text) can be tested by the developer. For features that are more subjective (eg. learnability) the developer is far too familiar with the application to genuinely assess them. These principles need to be tested by users who are unfamiliar with the project.
The features that need to be tested will depend on the useability requirements and respective criteria determined during the Explore phase.
Accessibility#
Some accessibility principle features that may be tested:
Perceivable: Information and user interface components must be presented to users in ways that they can perceive.
Operable: User interface components and navigation must be operable to users in ways they can operate.
Understandable: Information and user interface operation must be understandable.
Robust: Content must be robust enough so that it can be interpreted reliably by a wide variety of users and types of assistive technologies.
Effectiveness#
Some effectiveness principle features that may be tested:
Can a user interact with a digital solution quickly and easily
Are outputs presented clearly in a way that can be easily interpreted
Is the application reliable (constant, dependable, consistent and repeatable).
Safety#
Get feedback from the tester on safety principles features the following questions could be asked:
Is there sufficient instructional information?
Are there too many steps involved?
Are there unexplained abbreviations, initializes, or acronyms?
Does it display sufficient content to allow users to act?
Are all object labelled clearly and accurately?
Is information organize clearly?
Is necessary information displayed?
Are input boxes should be wide enough for users to see and edit their input?
Are there and misleading cues to click?
Are the phrasing of menu items and buttons familiar and consistent?
Are important items placed consistently?
Is important information highlighted.
Is user data entry minimize
Is visual clutter minimize so that attention is drawn to important information?
Are lists ordered appropriately?
Is there adequate and informative feedback?
Utility#
To test for the utility of the application, you need to assess if the testers have been provided all the functionality that they need. They could be asked if there is functionality missing, or if they would expand some current functionality.
Learnability#
In testing the learnability principles features, the tester needs to be asked quickly and easily they could:
Find information
Complete tasks
Navigate the digital solution
