Develop Introduction
Contents
Develop Introduction#
Tools used to complete the Develop phase:
Mockups
Class Diagrams
IPO Tables
Pseudocode
Desk-checking
Data Flow Diagrams
Entity Relationship Diagrams
Relational Schemas
Overview#
The develop phase involves students creating new understanding and identifying possible solutions using design, systems, and abstraction and algorithmic computational thinking processes. Students evaluate personal, social and economic impacts, components and digital solutions against criteria throughout the develop phase to make decisions and refine the user experience and technical operation of components of the solution [QCAA, 2017].
To complete the Develop phase of the EDGE problem solving processes we will need to develop three distinct aspects of the application:
User Interface
Programming Components
Data Structure.
These three aspects reflect the MVC architecture pattern.
MVC architecture pattern#
The MVC architecture pattern turns complex application development into a much more manageable process. It is example of modularization and decomposition.
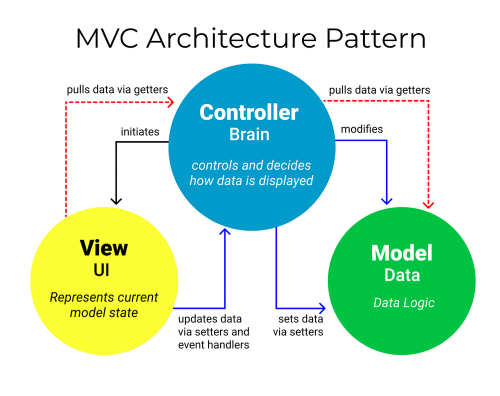
MVC stands for model-view-controller. Here’s what each of those components mean:
Model: The backend that contains all the data logic
View: The frontend or user interface (UI)
Controller: The brains of the application that controls how data is displayed
Why use MVC?#
We use MVC to establish separation of concerns(SoC).
The MVC pattern helps you break up the frontend and backend code into separate components. This way, it’s much easier to manage and make changes to either side without them interfering with each other.
But this is easier said than done, especially when several developers need to update, modify, or debug a full-blown application simultaneously.
Model (Data)#
The model’s job is to simply manage the data. Whether the data is from a database, API, JSON object or local file, the model is responsible for managing it.
Views (UI)#
The view’s job is to decide what the user will see on their screen, and how.
Controller (Brain)#
The controller’s responsibility is to pull, modify, and provide data to the user. Essentially, the controller is the link between the view and model.
Through getter and setter functions, the controller pulls data from the model and initializes the views.
If there are any updates from the views, it modifies the data with a setter function.
To develop ideas, students:
use design thinking to visualise ideas and synthesise information and ideas in response to a digital problem by using drawing and creative skills to represent and communicate ideas
acquire required information, tools and skills to implement a solution plan
use computational thinking to apply abstraction procedures to problem components
use computational thinking to express algorithms
use systems and design thinking to develop ideas about components and solutions to test conceptual models
use systems and design thinking to generate creative ideas, identify a solution and evaluate ideas that best meet the criteria for success. [QCAA, 2017]
