Develop Data Store
Contents
Develop Data Store#
Tools used to complete the Develop phase:
Data Flow Diagrams
Entity Relationship Diagrams
Data Dictionaries
Relational Schemas
For Units 1#
Data Stores are not addressed in Unit 1. For the purposes of developing your solution, you need to consider two things:
What data will you need to collect and keep temporarily (whilst the program is running)
What data will you need to load from or save to a file.
This information can be add to your mind map.
For Units 2 to 3#
For units 2 to 3 the Model component of the MVC Architecture (datastore) is going to be a database. You will be responsible for the designing of this database.
To design the database we will follow the steps outlined in the diagram below down to in the tasks steps in green (Data Dictionary and Relational Schema)
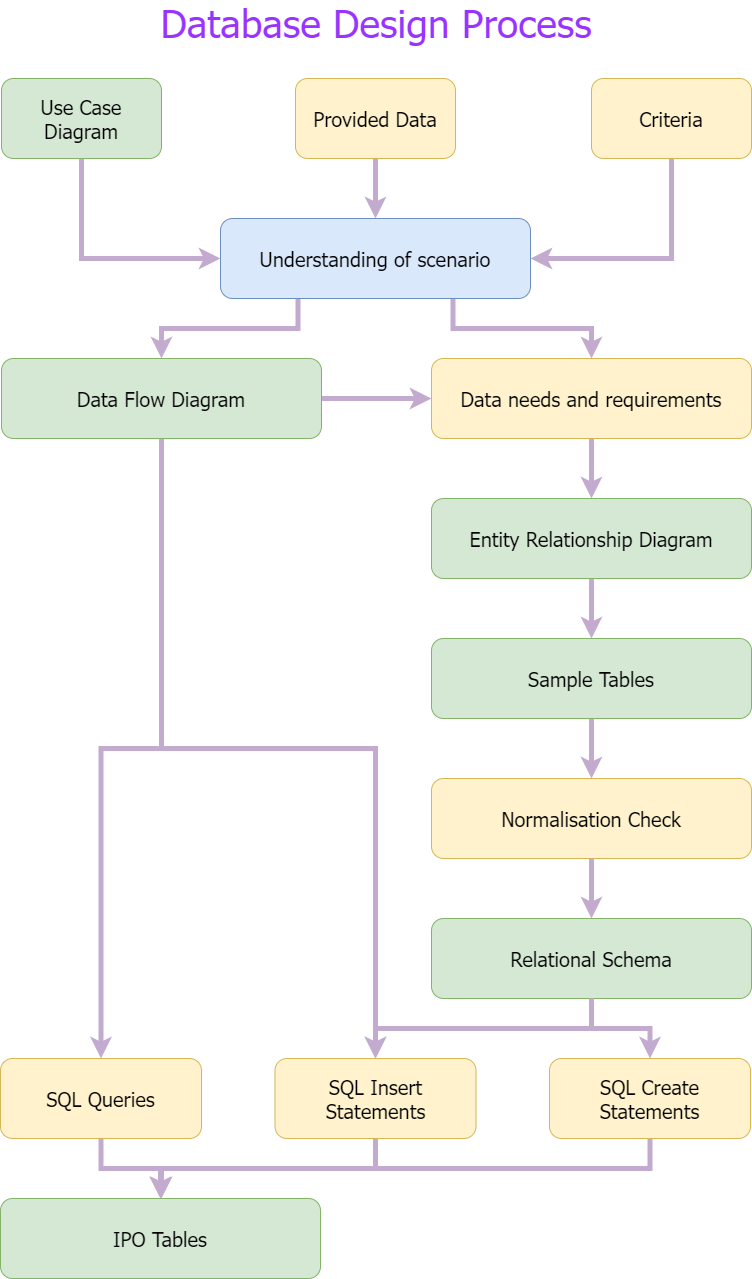
Steps for creating a DFD#
Step 1: Identify the External Entities
Step 2: Identify Processes
Step 3: Identify Data Stores
Step 4: Identify Data Flows
Step 5: Decompose to next level
Steps for creating a ERD#
Step 1: Identify the entities
Step 2: Add attributes
Step 3: Establish relationships and cardinality
Step 4: Resolve many-to-many relationships
Step 5: Identify the foreign keys
Rules for normalisation of database#
1st Normal Form (1NF)
Each column should contain atomic values
Each column should contain the same type of data
Each column should have a unique name
The order in which the data is saved does not matter
2nd Normal Form (2NF)
Is in 1NF
There are no partial dependencies:
3rd Normal Form (3NF)
Is in 2NF
There are no transitive dependencies:
Data dictionaries#
Create a data dictionary for each database table detailing the following field attributes:
Name of Field
Definition of the Field
Data type (Text, Integer, Real, Blob)
Possible values (taken from sample data)
Validation rules (NOT NULL, DEFAULT, UNIQUE, PRIMARY, CHECK)
Formatting (to be applied in the front end)
Relational Schema#
The Relational Schema is the final ERD where the Data Type for each field has been identified.
Unit 2 subject matter covered:
recognise data types, constraints, and primary and foreign keys
symbolise the links between external entities, data sources, data flow, processes and data storage in annotated context diagrams or data flow diagrams
understand SQL syntax and use SQL statements to solve a problem
understand that data is organised in tabular form and the skills and knowledge used to normalise and link tables together
understand the reasons and methods of database structure modification to third normal form (3NF)
interpret the structure of a database represented by a relational schema (RS) to determine the relationship between data
explain data principles including acquisition, organisation, representation, integrity, redundancy, and security
explain the difference between data validation and data verification
explain referential integrity, normalisation and third normal form, relational database management system
explain the difference between primary key and foreign key
explain relations (tables) including rows; columns; primary, secondary and foreign keys; nulls; and views within a database management system
symbolise data flow through a system using data flow diagrams
analyse and structure data and data stores to reduce redundancy and ensure completeness, consistency and integrity for use and storage
apply data management processes, e.g. encryption, consistency, searching, pattern recognition and de-identification
determine appropriate data types, constraints, and primary and foreign keys
evaluate and modify a database structure to third normal form (3NF) [QCAA, 2017]
Unit 3 subject matter covered:
symbolise, explain and use advanced data processes, including table joins, referential integrity, redundancy reduction and anomaly updating
apply data algorithms for cleaning and merging data sources and iterating through data records
Unit 4 subject matter covered:
recognise and describe encryption and authentication strategies appropriate for securing data transmissions and their differences
recognise and describe features of symmetric (Data Encryption Standard — DES, Triple DES, AES — Advanced Encryption Standard, Blowfish and Twofish) and assymetric (RSA) encryption algorithms
recognise and describe how data compression, encryption and hashing are used in the storage and transfer of data
explain Australian Privacy Principles (2014) and ethics applicable to the use of personally identifiable or sensitive data from a digital systems perspective
explain network transmission principles, including latency, jitter, guarantee and timeliness of delivery, and protocols relevant to the transmission of data over the internet, e.g. HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, VPN, streaming and broadcasting data packets
explain methods for data exchange used to transfer data across networked systems including REST, JSON and XML
symbolise, analyse and evaluate Caesar, Polyalphabetic (e.g. Vigenere and Gronsfield), and one-time pad encryption algorithms
describe data using appropriate naming conventions, data formats and structures
symbolise and explain secure data transmission techniques and processes, including the use of encryption, decryption, authentication, hashing and checksums [QCAA, 2017]
