Develop Algorithms
Contents
Develop Algorithms#
Tools used:
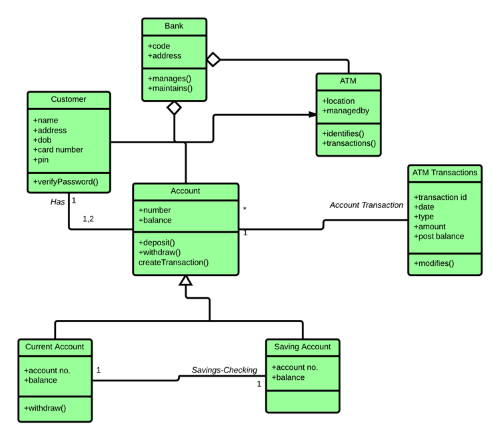
Class Diagrams
Pseudocode
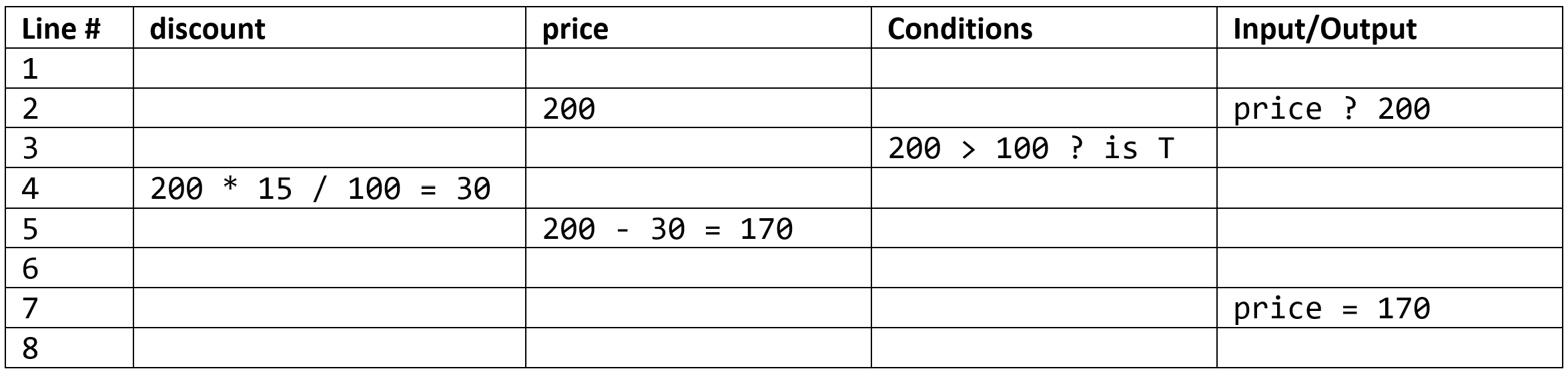
IPO Tables
Desk-checking
For Unit 1 to 4#
Algorithms are the heart of your program, so we spend a bit of effort in designing them.
You will use the following tools to design your algorithms. You will work with them in no particular order, and will most likely move back a forth between them.
Class Diagram#
IPO Tables#

Desk Checking#
For Units 2 to 4#
In additional to the requirements from Unit 1, for Units 2 to 4 you will need to create IPO tables for the operation of the Database.
Specifically you will need tables for:
Creating the database
Processing data for insertion
Manipulation of data
Retrieval of data
Unit 1 subject matter covered:
recognise and describe programming syntax and rules
understand that simple algorithms consist of input, process and output at various stages
understand and use assignment, sequence, selection, condition, iteration, and modularisation
represent algorithms using pseudocode by identifying and describing the steps and their behaviour in the algorithm
represent algorithms using pseudocode by identifying and explaining the algorithmic steps required for a programmed solution
symbolise algorithms and interrelationships with sketches and diagrams
understand the five basic features of programming – variables, control structures, data structures, syntax and libraries and classes.
recognise, describe and use good programming practices, including dependability, efficiency, testing, debugging, error correction, coding conventions including commenting, consistent naming conventions, code simplicity and portability
identify and describe the purpose of code syntax and rules
identify and describe the scope and use of local and global variables
identify and describe code object/event triggers and their effect on user interfaces [QCAA, 2017]
Unit 2 subject matter covered:
symbolise well-ordered and unambiguous algorithms using pseudocode for procedural code that processes data for insertion into a database or manipulates or displays retrieved data
symbolise well-ordered and unambiguous algorithms using pseudocode for user interaction, data validation and data presentation [QCAA, 2017]
Unit 3 subject matter covered:
recognise and describe program components such as objects, event handlers and multimedia assets
recognise and describe external data stores such as file structures or object libraries
recognise and describe internal data structures such as arrays, lists and dictionaries
analyse modularity and readability of program modules
apply computational thinking processes, e.g. creating, debugging, persevering and collaborating to identify possible algorithmic approaches [QCAA, 2017]
Unit 4 subject matter covered:
symbolise and explain how application sub-systems, e.g. front end, back end, work together to constitute a solution
develop simple Caesar, Polyaphabetic (e.g. Vignere and Gronsfeld), and one-time pad encryption algorithms
evaluate by desk checking algorithms to predict the output for a given input, identify errors and validate algorithms [QCAA, 2017]
