Analyse the Problem
Contents
Analyse the Problem#
Tools used:
mind maps
UML Use Case Diagram
For Units 1 to 4#
To analyse the problem we use our understanding of computational thinking and systems thinking to decompose the problem and define the scope.
We use mind maps to create a basic sketch of our understanding of the problem.
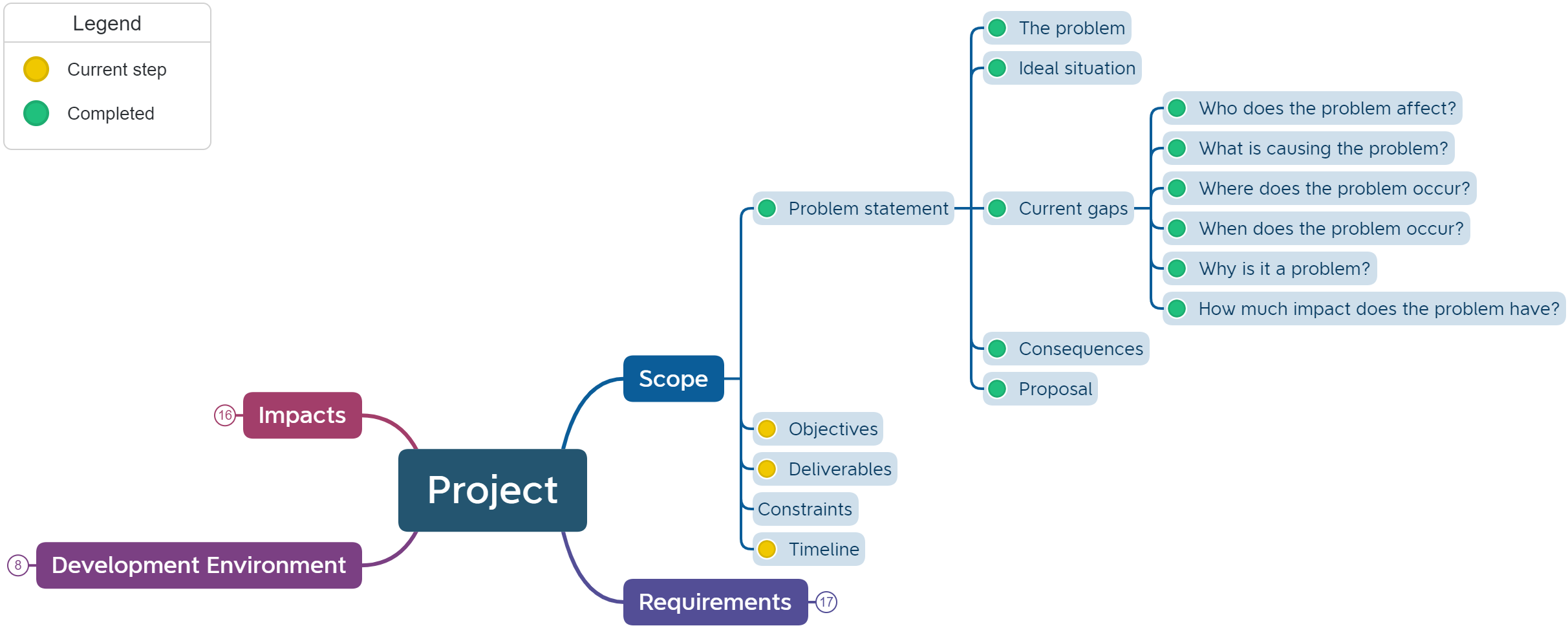
We use the UML Use Case Diagram to help identify the scope of the program and the processes involved.
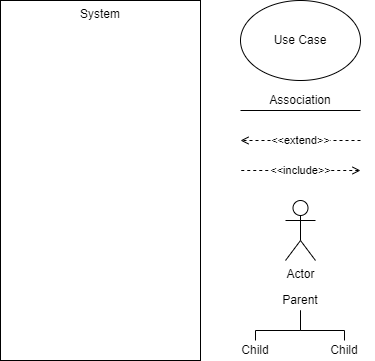
For Units 2 to 4#
In addition to the requirements of Unit 1, you need to be cafeful with the representation of databases in the Use Case Diagram.
Type of Database |
Use Case Representation |
|---|---|
Internal |
Databases are not considered an actor and are included within the system box |
External |
Databases are considered an actor and are drawn as a secondary actor |
Unit 1 subject matter covered:
understand methods of breaking down problems into parts using computational thinking and thinking tools
analyse problems to identify essential elements, components and features of problems in Digital Solutions
analyse problems to identify where and how digital technologies are used to solve problems to meet personal, societal and organisational needs
explore existing solutions to similar problems
analyse a given problem to identify the boundary or scope of the problem
analyse a given problem to identify missing, required or unnecessary facts or information [QCAA, 2017]
Unit 3 subject matter covered:
analyse a problem to identify and explain the elements of a system, the observable interactions, the inputs and outputs, the control mechanism, and the processes and interactions using logical diagrams and consistent symbols
analyse problems and information to determine manageable aspects of the problem,
analyse problems and information to determine a specific aspect of the problem to develop
analyse problems and information to determine and describe interactions in terms of inputs, processes and outputs
analyse problems and information to determine and explore data sources to understand relational and flat file data structures
recognise and compare different file formats and data structures appropriate to the context
determine file formats and data structures appropriate to the technology context [QCAA, 2017]
Unit 4 subject matter covered:
analyse problems and information to determine necessary coded modularity and features
analyse problems and information to determine factors and risks that affect data security, including confidentiality, integrity and availability, and privacy
analyse problems and information to determine existing code within inbuilt libraries
determine manageable aspects of a problem through a decomposition and analysis of risks
determine manageable aspects of a problem through a decomposition and analysis of available tools and code libraries
determine manageable aspects of a problem through a decomposition and analysis of data interface
determine data sources required to generate data components [QCAA, 2017]
