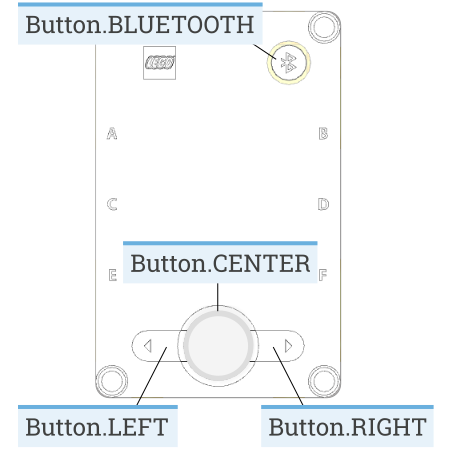
Hub Inputs¶
Pybrick Documentation
To explore all Pybricks’ features check the Pybricks documentaion. This can also be seen in the right-hand panel of the Pybricks IDE.
The Prime Hub has two features that can provide input to the robot
buttons
inertial measurement unit (IMU)
IMU¶
The IMU is a sensor that can detect how the robot is moving. The sensor is configured around the x-axis, y-axis and z-axis as indicated in the image below.
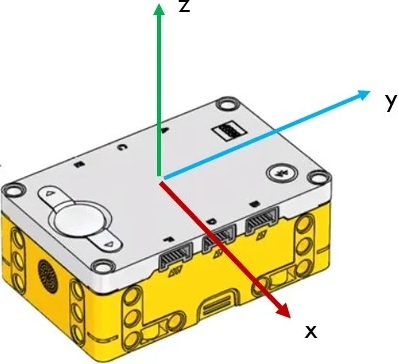
Rotation along each axis has a specific name:
Roll is rotation along the x-axis
Pitch is rotation along the y-axis
Yaw is rotation along the z-axis, but it is not yet implemented.
IMU Orientation Functions¶
Pybricks offers two functions that informs the hub’s orientation:
imu.up()→ Side→ Checks which side of the hub currently faces upward.side values are:
Side.TOP
Side.BOTTOM
Side.LEFT
Side.RIGHT
Side.FRONT
Side.BACK.
imu.tilt()→ Tuple[int, int]→ Returns the pitch and roll angles in a tuple (pitch, roll)
IMU Orientation Example¶
Use the code below to explore how these functions works.
Create a new file called
imu_orientation.pyType the code below into the file
Predict what you think will happen.
Run your code
1from pybricks.hubs import PrimeHub
2from pybricks.pupdevices import Motor, ColorSensor, UltrasonicSensor, ForceSensor
3from pybricks.parameters import Button, Color, Direction, Port, Side, Stop
4from pybricks.robotics import DriveBase
5from pybricks.tools import wait, StopWatch
6
7# --- SETUP
8# start components
9hub = PrimeHub()
10
11# store variables
12
13# --- RUNNING
14while True:
15 # read sensor data
16 up = hub.imu.up()
17 pitch, roll = hub.imu.tilt()
18
19 # process data
20
21 # output data
22 print(up, "\t", pitch, "\t", roll)
Investigate
lines 3 - 7 → imports all the Pybricks command for use with your robot
line 10 → initialised the hub
line 13 → creates an infinite loop
line 14 → gets which side of the hub is facing up and stores it in
upline 15 → gets the tuple containing the tilt values, stores the first tuple value in
pitchand the second tuple value inrollline 17 → prints the values of
up,pitchandrollto the Pybricks terminal
Modify
what is the highest and lowest roll value you can get?
what is the highest and lowest pitch value you can get?
what happens if you remove both
"\t",from line 17?